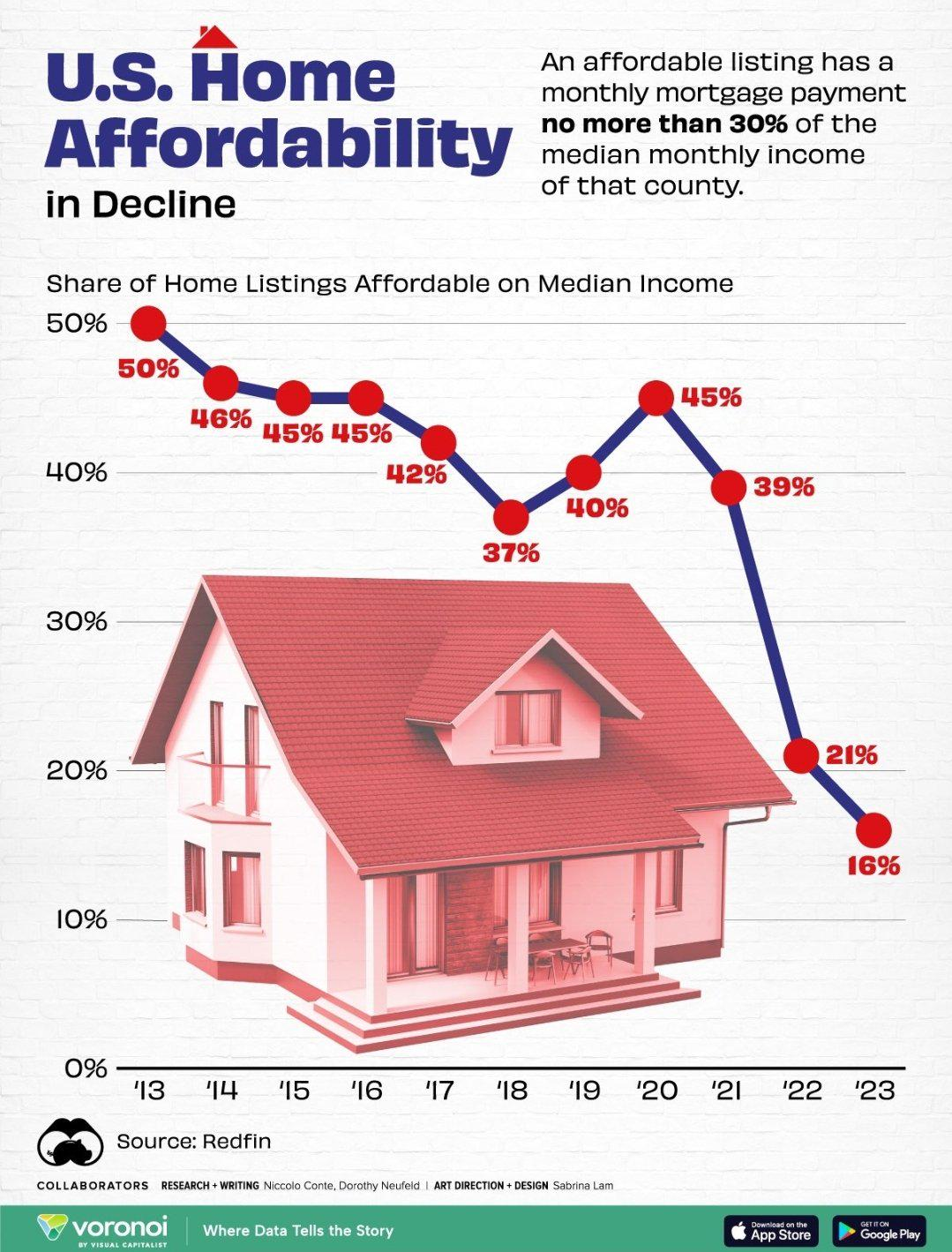
The United States is grappling with a growing housing affordability crisis that puts homeownership out of reach for an increasing number of families. As home prices have soared, exacerbated by construction productivity challenges, many Americans struggle to find affordable options in the current housing market. The effects of NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies and stringent land-use controls have added layers of complexity to this urgent issue, stifling the number of new homes being built and inflating prices further. Additionally, housing market regulations often hinder innovative practices that could alleviate costs, posing significant homeownership challenges for new buyers. Addressing these intertwined factors is crucial for creating sustainable progress towards more accessible and affordable housing for all citizens.
The ongoing crisis in affordable housing has surfaced as a critical issue in contemporary America, jeopardizing the fundamental right to homeownership for millions. Various elements, including local opposition to new developments and restrictive land-use regulations, serve to hinder construction efficiencies and limit available options on the market. As we delve into this pressing topic, it becomes evident that the growth of housing supply is essential in combating the current challenges associated with housing costs. Understanding the impacts of community policies and construction dynamics will shed light on potential pathways to enhance residential accessibility. This discussion will highlight the importance of evaluating regulations and embracing innovative solutions to improve housing availability for everyone.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis has emerged as a significant issue across the United States, with home prices skyrocketing beyond the reach of many prospective buyers. Factors leading to this situation include economic variables such as rising labor costs and material shortages, but an often-overlooked culprit is the impact of 22not in my backyard 22 (NIMBY) policies. These regulations limit housing development and increase costs, thus contributing to a market where homeownership is increasingly unattainable for many families.
As the cost of constructing new homes continues to rise, the American dream of homeownership diminishes for a large segment of the population. The restrictions imposed by NIMBY policies not only slow down the construction process but also stifle innovation within the housing market. This stagnation in productivity has resulted in a persistent housing shortage, evident in the soaring prices that many first-time buyers face today.
The Impact of NIMBYism on Housing Prices
NIMBY policies have fundamentally reshaped the landscape of American housing by creating a framework where community opposition to new developments hinders construction efforts. As homebuilders navigate complex regulations and zoning laws aimed at restricting project sizes and types, the practical consequences manifest in limited housing inventory. Fewer homes being built inevitably leads to higher prices, cementing the crisis of affordability for homebuyers.
Moreover, an increase in land-use controls directly correlates with a decline in construction productivity. A striking example is the comparison of large-scale developments from the mid-20th century with today’s projects, which are often smaller and constrained by stringent guidelines. Builders who once managed vast tracts of land have been reduced to working within overly restrictive local regulations, decreasing the overall housing stock and inflating prices.
Construction Productivity and Market Regulations
Construction productivity has seen a dramatic decline since the 1970s, a trend that aligns with the rise of comprehensive housing market regulations. Builders have been forced to adapt to a landscape marked by localized land-use controls that prioritize community preferences over the necessity of expanding housing availability. This not only limits the size of projects but also diminishes firms’ motivation to innovate within the building sector.
As highlighted by economist Edward Glaeser, the productivity of housing construction has stagnated, starkly contrasting with the progress seen in other industries such as automotive manufacturing. The failure to embrace economies of scale due to restrictive regulations has led to reduced output per employee in the construction sector, compounding the challenges faced by those seeking affordable homes in today’s market.
Homeownership Challenges in Today’s Economy
The decline in homeownership rates among younger generations exemplifies the challenges presented by high housing costs and stagnating wages. Economic factors such as low inventory, inflated property values, and the burden of student debt contribute to a landscape where aspiring homeowners find it increasingly difficult to enter the market. Moreover, the repercussions of land-use regulations further complicate this scenario, effectively shutting down opportunities for first-time buyers.
Many young professionals are now delaying their homeownership dreams not only due to high prices but also because of the complexities introduced by housing market regulations that seem to hinder, rather than help, the expansion of affordable housing options. As the gap between income levels and housing prices widens, this group faces a growing homeownership challenge that could have lasting effects on their economic security.
The Role of Innovation in Housing Construction
Innovation plays a pivotal role in lowering construction costs and improving housing affordability. However, the stagnation in the construction sector’s productivity has resulted in a stark divergence from other industries that have leveraged technological advancements to boost output. For instance, while companies in manufacturing have seen significant productivity gains, construction firms have been hampered by policies that stifle the development of efficient building techniques.
The failure to innovate within the construction sector can be attributed to the increasing prevalence of NIMBY policies that create an environment of risk aversion among builders. Without the incentive to develop cost-saving innovations, the industry remains trapped in a cycle of high prices and low output, ultimately exacerbating the existing housing affordability crisis.
The Future of Housing Market Regulations
As we look towards the future, the need for reform in housing market regulations becomes increasingly apparent. With the interplay of NIMBY practices and land-use controls contributing to rising costs, policymakers must consider pathways to balance community concerns with the pressing demand for affordable housing. This might involve streamlining permitting processes, incentivizing larger developments, and promoting zoning reforms that encourage higher density dwelling.
Regulatory changes could foster a construction environment that embraces innovative building methods, paving the way for a more responsive housing market. By aligning regulations with the goal of expanding housing availability, the future could see a shift in the current paradigm that has left many Americans priced out of homeownership, ultimately alleviating the housing crisis facing the nation.
Breaking Down Land-Use Controls
Land-use controls epitomize the regulatory barriers that present significant obstacles in housing construction. These regulations often reflect the vested interests of existing homeowners who resist changes that could alter the character of their neighborhoods. While community input is essential, the current rigidity of these controls often prioritizes exclusion over accessibility, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis.
Reform of land-use regulations is critical to breaking down the barriers that limit housing supply. By adopting a more flexible approach to zoning, municipalities can enable larger developments and encourage builders to invest in innovative construction techniques. Such changes could help to restore balance in the housing market, where supply and demand can harmonize to ensure affordability for those seeking homes.
The Economic Dynamics of Housing Supply and Demand
Understanding the economic dynamics of housing supply and demand reveals the interconnected challenges that contribute to the housing affordability crisis. As demand continues to outpace a stagnating supply, prices inevitably rise, locking many potential buyers out of the market. Factors such as rising interest rates, coupled with high construction costs driven by NIMBY policies, create a perfect storm that complicates the landscape of homeownership.
The economic principles of supply and demand highlight the necessity for increased building activity to stabilize prices. However, with current construction productivity levels hampered by burdensome regulations, the imbalance in the housing market remains a formidable challenge. Addressing these barriers through comprehensive reform could foster a more dynamic and responsive housing environment.
The Intergenerational Transfer of Housing Wealth
A significant consequence of the housing affordability crisis is the intergenerational transfer of wealth that disadvantages younger generations. As older homeowners accumulate wealth through property appreciation, younger individuals find themselves unable to enter the market, resulting in economic disparities that affect their long-term financial security. This transfer not only perpetuates wealth inequality but also reinforces the barriers to homeownership.
As Glaeser highlights, the shift in housing wealth from one generation to another often leaves younger earners at a severe disadvantage, manifesting in lower rates of home equity and increased challenges in housing accessibility. Addressing this dynamic requires concerted efforts to reform housing policies that prioritize equitable access to homeownership opportunities, thereby breaking the cycle of economic disparity.
Strategies for Addressing Housing Inequality
To effectively tackle housing inequality, a multifaceted approach is necessary that incorporates policy reform, community involvement, and innovative building practices. One key strategy involves revisiting zoning laws that currently restrict the types and sizes of housing developments. By allowing for greater density and diverse housing options, municipalities can help mitigate the supply crunch that has been driving prices up.
Additionally, engaging communities in open discussions about the necessity of new housing developments can foster cooperation between homeowners and builders. By addressing concerns transparently and emphasizing the benefits of increased housing availability, it’s possible to cultivate a culture that values inclusivity over exclusion, ultimately paving the way for a more equitable housing market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do NIMBY policies play in the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies significantly contribute to the housing affordability crisis by imposing strict land-use regulations that restrict new housing developments. These policies can lead to smaller, individualized projects rather than large-scale construction, reducing productivity and innovation in the housing market. By limiting the size and scale of construction, these regulations increase the cost of housing, making homeownership unattainable for many Americans.
How do land-use controls impact housing affordability?
Land-use controls directly affect housing affordability by limiting the availability of land for new housing developments. These regulations can slow down construction and lead to fewer housing units being built, which exacerbates the housing affordability crisis. As a result, the increased demand for limited housing stock drives prices up, making it harder for people to buy homes.
What are common homeownership challenges related to housing market regulations?
Homeownership challenges related to housing market regulations include high costs due to land-use restrictions, prolonged development timelines caused by bureaucratic approvals, and limited availability of affordable housing options. These factors make it difficult for potential homeowners to enter the market, contributing to the ongoing housing affordability crisis.
How does construction productivity affect the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity has a significant impact on the housing affordability crisis. When productivity is low, fewer homes are built, and construction costs rise. Recent studies indicate that increased land-use regulations and NIMBY policies have stifled construction productivity, resulting in higher prices for new homes and further limiting access to homeownership for many Americans.
What is the relationship between land-use regulations and construction productivity?
There is a direct relationship between land-use regulations and construction productivity. Tighter land-use controls limit the size of housing projects, which often leads to smaller, less efficient construction firms. This decrease in scale can hinder innovation and ultimately lead to lower productivity, contributing to the housing affordability crisis as fewer homes are produced to meet rising demand.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The rising cost of housing has made ownership unattainable for many Americans, with prices more than doubling since 1960. |
| Impact of Land-Use Regulations | Tight land-use controls are linked to declines in productivity within the construction sector, contributing to increased housing costs. |
| NIMBYism | ‘Not in my backyard’ attitudes have resulted in smaller building projects, limiting mass production and innovation in housing. |
| Construction Productivity | Construction productivity peaked between 1935 and 1970 but has steadily declined since, correlating with rising land-use regulations. |
| The Role of Large Builders | Large construction firms, which can build more efficiently, have decreased in number and size since the 1970s. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are accumulating significantly less housing wealth compared to older generations, exacerbating wealth inequality. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue impacting a growing number of Americans. The challenges stem from rising costs associated with homeownership, which have more than doubled since the 1960s, largely driven by restrictive land-use regulations and NIMBYism. As a result, the construction sector’s productivity has stagnated, limiting the ability to produce affordable housing at scale. To tackle this crisis, there needs to be a re-evaluation of housing policies that currently stifle innovation and increase costs, allowing for broader access to affordable housing solutions.