The impact of China tariffs on the global economy is a pressing issue that has ignited discussions among economists and policymakers alike. As tensions from the ongoing trade war with China escalate, the repercussions are not limited to Beijing’s economy but extend significantly to the U.S. economy as well. The implementation of aggressive tariffs threatens to drive up prices for American consumers, contributing to widespread supply chain disruptions that can ripple through various industries. As businesses grapple with these challenges, the durability of U.S. foreign relations becomes intertwined with how these tariff strategies unfold. Ultimately, the interplay of economic policies will shape not only domestic market conditions but also the geostrategic landscape between the United States and its global partners.
The ramifications of the proposed tariffs on Chinese imports are becoming increasingly apparent in the context of international trade dynamics. Current tensions are largely characterized by a growing economic confrontation, often referred to as a trade dispute with China. The potential levies could lead to higher costs for American households and businesses, while creating complexities across myriad supply chains that depend on Chinese manufacturing. Moreover, such policies could significantly alter the landscape of U.S. diplomacy and alliances, affecting relations with not just China but also key allies. As the situation evolves, understanding the wider implications becomes essential for navigating this multifaceted economic challenge.
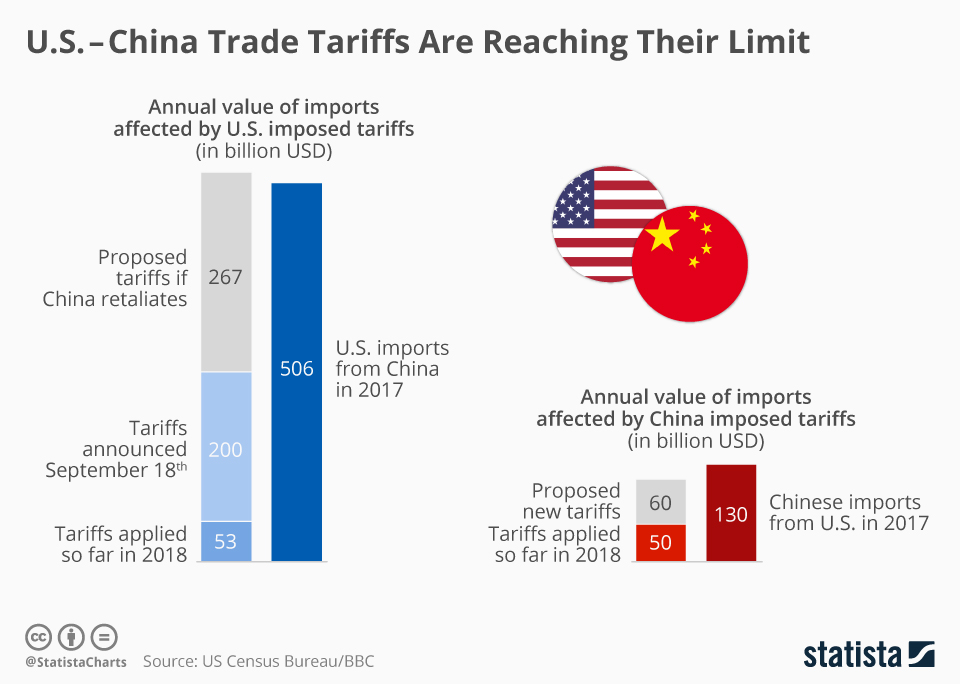
Understanding the U.S.-China Trade War
The ongoing trade war between the United States and China has evolved significantly, influenced by tariffs and economic strategies. At the center of this conflict are the tariffs imposed by the U.S. government, which aim to protect American industry but, paradoxically, may have far-reaching implications for U.S. foreign relations and the wider global economy. Experts argue that China is adapting to these challenges, seeking to bolster its own economy while reevaluating its relationships with traditional allies of the U.S. The interplay between these economic strategies is crucial for understanding the future of international trade.
As tariffs continue to play a pivotal role in this geopolitical discussion, they affect not only the direct economic exchanges but also the complicated network of alliances and partnerships that characterize U.S. foreign relations. The imposition of tariffs signals more than just an economic policy change; it represents a shift in diplomatic relations, potentially pushing China closer to its allies and creating a unified front against U.S. pressure. This unique position complicates the prospects for a resolution, as stakeholders on both sides must navigate these evolving economic landscapes.
The Economic Ripples of China Tariffs Impact
The impact of tariffs on Chinese goods can resonate throughout the U.S. economy, particularly affecting consumer prices and supply chains. Industries reliant on imports from China may face increased costs, which could lead to higher prices for American consumers. This scenario raises critical questions about inflation and economic stability as consumers begin to feel the pinch in their wallets. The challenge will be to manage these price increases without triggering greater economic disruption, which could have cascading effects on the overall health of the U.S. economy.
Moreover, the potential for supply chain disruptions is a particularly concerning aspect of escalating tariffs. With many U.S. companies deeply embedded in the global supply chain, a tariff-driven alteration could result in shortages or delays in product availability, further straining both consumers and businesses alike. The sectors most vulnerable to these impacts include technology and consumer goods, where the dependence on Chinese manufacturing is substantial. As companies scramble to adapt, some may seek alternative suppliers, potentially realigning global trade patterns in response to these tariffs.
China’s Response to Potential Tariffs
In anticipation of potential tariff increases, Beijing’s strategic response reflects a mix of cautious optimism and significant concern. On one hand, Chinese policymakers are exploring various avenues to mitigate the impact of tariffs, including strengthening ties with other trading partners to lessen their dependence on the U.S. markets. This includes ramping up efforts to penetrate emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Africa as part of their long-term strategy.
Conversely, the uncertainty surrounding U.S. tariffs presents a significant challenge for Chinese businesses and the economy at large. With domestic demand waning and the housing market struggling, any further embedding of tariffs could exacerbate these downturns. Concerns about how tariffs will be structured and imposed add layers of complexity to trade negotiations, making it imperative for China to adopt a flexible, adaptive strategy to maintain its economic foothold globally.
Potential Implications for Global Supply Chains
Changes in U.S. tariff policies will invariably have a profound effect on global supply chains. Industries that have depended heavily on Chinese imports must now evaluate their sourcing strategies, which may involve relocating production or diversifying their supply sources. This shift could have lasting ramifications not only for U.S. manufacturers but also for exporters in countries like Vietnam and India, who may find new opportunities to fill the gaps left by China.
Additionally, these global supply chain adjustments trigger strategic movements in foreign investments and partnerships. As U.S. tariffs against China become a reality, countries that can rapidly adapt and provide alternative supply chains may emerge as invaluable partners for American companies, potentially reshaping global trade dynamics. This situation presents an intriguing paradox: as the U.S. imposes tariffs to enhance domestic protection, it may, in turn, encourage the globalization of production elsewhere.
Examining Labor Market Effects During the Trade War
The labor market in the United States is intricately tied to the policies enacted around tariffs, particularly those aimed at China. Trade restrictions can lead to immediate job losses in industries adversely affected by increased costs or supply chain disruptions. However, the potential for job creation exists in sectors that pivot to meet changing demands or that relocate operations to avoid tariffs. This dual-edged sword illustrates the complexities in assessing the net impact of tariffs on employment.
At the same time, the potential for labor shortages is becoming increasingly relevant, especially in key industries that rely on imports from China. As companies look for alternatives, they may face challenges in transitioning their workforce to new production methods or suppliers. The growing skills gap in the labor market becomes critical in this context, emphasizing the necessity for retraining programs to prepare workers for evolving job demands amidst the turbulent landscape of U.S.-China relations.
Future of U.S.-China Relations Amidst Economic Tensions
As tensions escalate in the U.S.-China trade relationship, the long-term implications for foreign relations and economic partnerships remain uncertain. The likelihood of continued tariffs suggests a protracted period of economic rivalry, with both nations realigning their diplomatic strategies in response to one another’s actions. This situation raises concerns among other countries about which side to support, as alliances may be influenced by trade dynamics rather than traditional political ideologies.
Furthermore, the evolving nature of these tensions could lead to unexpected economic coalitions. Countries in the European Union, for example, might find common ground with China in opposing U.S. tariffs, further complicating the landscape of global trade. The challenge for policymakers in the U.S. will be to navigate these developments while working to maintain relationships with traditional allies that may be swayed by shifts in economic ties.
China’s Strategic Market Diversification Efforts
In response to the trade pressures and market fluctuations caused by potential U.S. tariffs, China has actively pursued diversification of its export markets. By focusing on emerging economies in places like Southeast Asia and Africa, China is employing a multifaceted approach to bolster its economic security. The Belt and Road Initiative serves as a framework for these efforts, emphasizing infrastructure development as a means of establishing stronger economic ties beyond the U.S. market.
This diversification strategy not only aims to offset losses that could stem from decreased U.S. imports but also positions China to capture new markets. As trade routes evolve and new technologies are developed, Chinese businesses have the opportunity to secure a competitive edge in various sectors, particularly in renewable energy and technology-driven goods. The success of these strategies will significantly influence China’s long-term economic prospects and geopolitical influence.
Navigating Future Trade Policies and Strategies
As the trade war unfolds, the future of trade policies in the U.S. remains uncertain. Economists suggest that the potential for increased tariffs could compel American businesses to rethink their strategies in favor of domestic manufacturing or investing in alternative markets. The challenge lies in balancing these initiatives while keeping prices manageable for consumers and ensuring the stability of the labor market.
Additionally, as policymakers contemplate future tariffs, the focus will likely be on creating a more sustainable trade framework that considers global supply chains and international labor standards. This cooperative approach could foster a healthier economic climate, promote transparency in trade agreements, and ultimately strengthen U.S. foreign relations instead of isolating the country amidst rising protectionism.
Lessons Learned from Past Tariff Implementations
The history of tariffs implemented in the U.S. offers valuable insights into their potential effects on both domestic and foreign economies. Analyzing past trade disputes can shed light on the unintended consequences that tariffs may bring about, including increased prices for consumers and retaliatory measures from trading partners. The lessons learned emphasize the importance of strategic planning and negotiation skills in trade relations.
Moreover, the examination of historical tariff strategies can inform future decisions, highlighting the need for a more collaborative and diplomatic approach. Engaging in trade discussions that prioritize mutual benefits might help alleviate some of the tensions inherent in tariff disputes, assisting both the U.S. and China in avoiding the economic pitfalls associated with a prolonged trade war.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy?
The impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy can be significant, leading to higher prices for American consumers on imported goods, supply chain disruptions, and potential labor shortages. Economists warn that increased tariffs may stifle U.S. economic growth and productivity, while also heightening tensions in U.S. foreign relations.
How could the trade war with China influence supply chain disruptions in the U.S.?
The trade war with China can lead to notable supply chain disruptions in the U.S. as companies may face increased costs and delays due to tariffs. This can result in inflationary pressures as businesses pass costs onto consumers, while also complicating logistics and sourcing, especially for products heavily reliant on Chinese components.
What are the potential consequences of increased tariffs on Beijing’s economy?
Increased tariffs could further weaken Beijing’s economy, which already struggles with issues like weak consumer demand and a declining housing market. A significant tariff on goods from China would challenge its export capabilities, forcing the Chinese economy to find alternative markets more vigorously.
How might U.S. foreign relations change as a result of China’s response to tariffs?
As a response to U.S. tariffs, China may strengthen its ties with traditional U.S. allies, such as those in Europe and Asia. A unified front among countries facing U.S. tariffs could lead to new alliances and trade agreements that may isolate the U.S. politically and economically.
Could China compensate for the economic impact of U.S. tariffs through other markets?
While China may seek to offset the economic impact of U.S. tariffs by expanding into other markets like the European Union or emerging economies, these markets currently represent a smaller share of its overall exports. Long-term strategies, like the Belt and Road Initiative, may help but will take time to yield substantial economic returns.
What countries are likely to benefit from reduced imports from China due to higher U.S. tariffs?
Countries such as Vietnam and India might benefit from reduced imports from China, as they have been working to establish themselves as alternative manufacturing hubs. However, they may face challenges in scaling up their production capabilities quickly enough to meet the gap left by China.
Are U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods likely to encourage higher prices for consumers?
Yes, imposing tariffs on Chinese goods is likely to lead to higher prices for American consumers as businesses increase prices to absorb the tariff costs. This inflationary effect can diminish consumer spending power and impact the overall U.S. economy.
How has the concept of tariffs affected the U.S.-China relationship?
The ongoing imposition and discussion of tariffs have exacerbated tensions in the U.S.-China relationship, creating uncertainty and potential retaliatory actions. This dynamic complicates diplomatic relations and may hinder cooperative efforts on broader international issues.
What are some longer-term impacts of a trade war with China on global supply chains?
A trade war with China could lead to a re-evaluation of global supply chains, with companies looking to diversify their production outside of China to mitigate risks. This shift may result in higher costs and longer lead times as businesses transition to new manufacturing locations.
Why are economists concerned about the potential 60% tariffs on Chinese goods?
Economists are concerned about the potential 60% tariffs on Chinese goods due to the severe economic strain it could place on the U.S. and Chinese economies alike. Such tariffs could increase supply chain disruptions, lead to higher consumer prices, and provoke retaliatory measures from China that could escalate trade tensions.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact of Tariffs on U.S. Economy | Higher prices for consumers, supply-chain disruptions, and potential labor shortages. |
| China’s Response to Tariffs | China may struggle economically but sees potential for new negotiations and alliances. |
| Impact on U.S.-China Relations | Increased tariffs could strain diplomatic ties and push China closer to European allies. |
| Challenges for Alternatives to China | Other countries like India or Vietnam could struggle to meet U.S. demand quickly due to lack of infrastructure. |
| Economic Preparation in China | China has been strategizing for the possibility of new tariffs, focusing on boosting domestic demand. |
Summary
The impact of China tariffs is significant and multifaceted, with potential repercussions for both the U.S. economy and its international relations. A shift towards higher tariffs could lead to increased prices for American consumers and challenge existing supply chains. Furthermore, as U.S.-China relations deteriorate, China may capitalize on the situation by strengthening ties with other nations, posing not just an economic risk but also a geopolitical one for the United States.