The housing affordability crisis in the U.S. has reached alarming levels, with many Americans struggling to secure a place to call home. Rising property prices, often attributed to labor and material costs, have created insurmountable barriers for prospective homeowners. Furthermore, land-use regulation and the prevalence of NIMBYism have exacerbated these challenges, stifling construction productivity and hindering the development of affordable housing options. Analyzing current housing market trends reveals a stark contrast to historical norms, as the number of homes produced per construction worker has seen a significant decline since the 1970s. As homeownership challenges intensify, the call for reform in land-use policies has never been more urgent, demanding innovative solutions to revive the housing sector and restore accessibility for all.
The crisis surrounding housing affordability reflects a deeper issue of accessibility and sustainability within the American real estate landscape. This predicament, often compounded by restrictive land-use policies and local opposition characterized by NIMBYism, highlights a shift away from large-scale, efficient construction practices that once defined the industry. The dramatic rise in home prices has resulted in severe homeownership challenges for many, particularly younger generations seeking stability. With the construction sector lagging in productivity, understanding the underlying factors driving these housing market dynamics is crucial. To forge a path forward, it is essential to explore new strategies that prioritize inclusivity and innovation in the housing development process.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
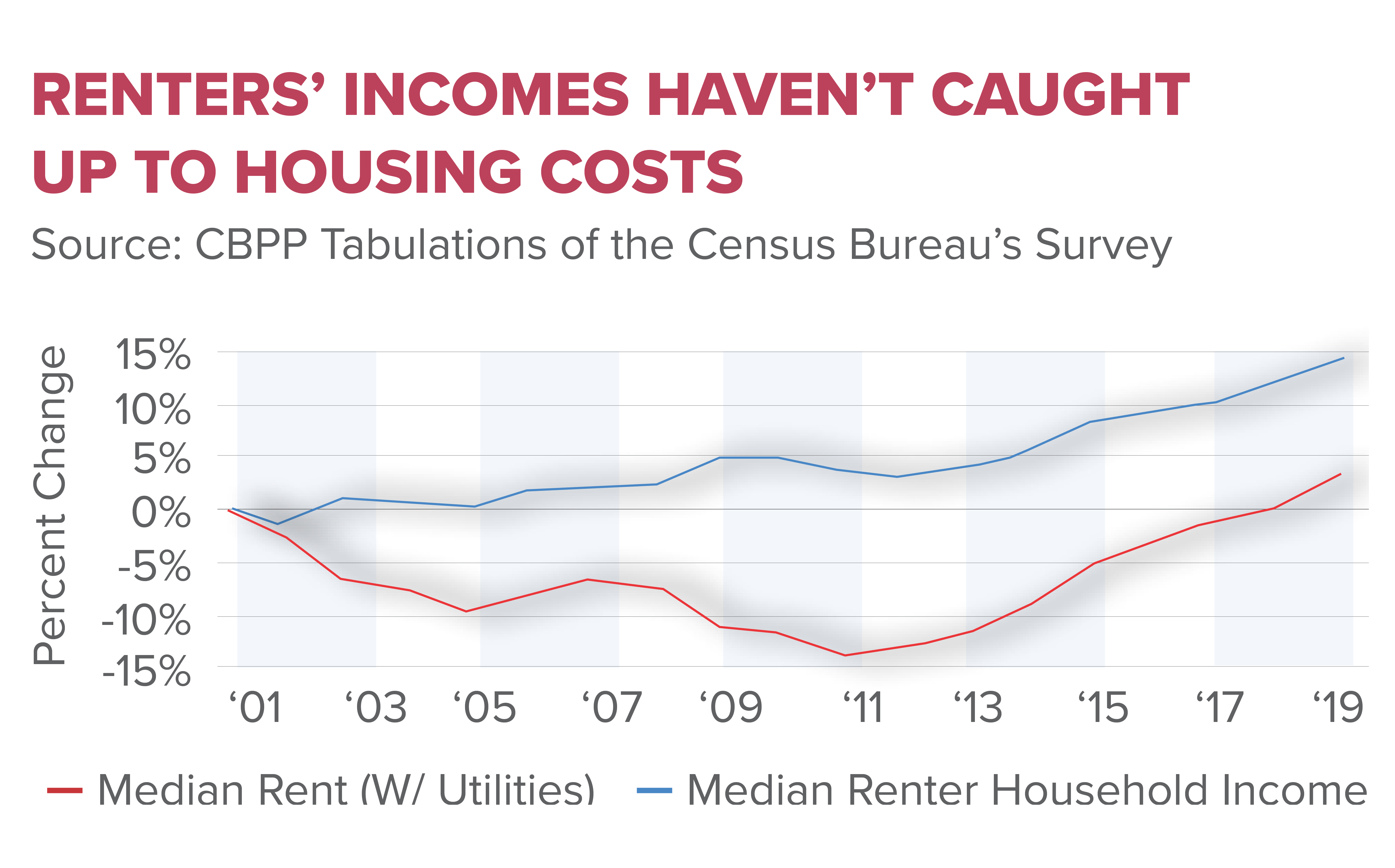
The housing affordability crisis has become a significant issue in the United States, leaving many Americans priced out of the market. This crisis emerged from a culmination of factors including escalating home prices, stagnant wages, and an increasing demand for housing. In particular, the rising costs associated with new homes have outpaced income growth, making it challenging for many to achieve homeownership. Statistics reveal that the price of a new single-family home has more than doubled since 1960, suggesting that the high cost of entry is not only a barrier but also a growing concern for the economic stability of families.
At the heart of this issue lies the impact of land-use regulation and local policies that often deter rather than encourage housing development. Regulations that constrain development sizes and complicate zoning have led to smaller projects that do not capitalize on economies of scale, making homes even more expensive. As historical data indicates, construction productivity has stunted since the 1970s when these regulations proliferated, thereby exacerbating the housing affordability crisis. Thus, a clear link exists between regulatory measures and the inability to meet housing demands effectively.
The Role of Land-Use Regulation in Housing Costs
Land-use regulation plays a pivotal role in shaping housing costs in American cities. Over the last few decades, stringent zoning laws and community-driven NIMBYism (Not In My Backyard) have limited the capacity for larger scale housing developments. Small lot sizes, restrictive building regulations, and the micromanagement of development projects have all contributed to this phenomenon. Builders are now often discouraged from pursuing larger, more cost-effective projects due to the complexities that arise, making it unaffordable for many prospective homeowners.
The inefficiencies caused by land-use regulation directly correlate with increases in housing prices. When builders focus on smaller projects, they work with reduced budgets and produce fewer homes that meet current demands. This approach not only raises costs but further limits market competitiveness and innovation in construction methods. Moreover, as evidenced by recent studies, areas with severe land-use regulations have seen decreased construction productivity, leading to a troubling trend where housing becomes less affordable as demand continues to rise.
Understanding NIMBYism and Its Impact on Development
NIMBYism reflects a critical challenge in the landscape of housing development; it is a social movement that prevents necessary housing projects from moving forward due to local opposition. Residents often resist developments not just due to concerns about aesthetics or community identity, but also because of fears of declining property values or changes to neighborhood dynamics. This localized resistance can erect substantial barriers to new housing initiatives, delaying development and perpetuating the housing affordability crisis.
The implications of NIMBYism extend beyond immediate community resistance. As local governments respond to voter sentiments against new housing projects, they inadvertently sustain a system of regulation that stifles productivity and innovation within the housing sector. The slowdown of large-scale developments has led to a constriction in the supply of housing options, ultimately driving up prices and limiting opportunities for homeownership among younger generations. As this trend continues, finding solutions that address both community concerns and housing needs remains essential.
Construction Productivity in Decline
Construction productivity has seen a notable decline since the 1970s, contrasting sharply with advancements in other sectors such as manufacturing. Historical data indicates that while industries like automotive manufacturing have achieved remarkable efficiency, the construction sector has struggled under the weight of increasingly complex regulations. The experience of builders today is vastly different from that of their post-war predecessors who capitalized on large-scale projects, where the economies of scale allowed for lower costs and mass-produced homes to be built. This shift highlights the critical barriers that contribute to stagnation and inefficiency in construction.
An important observation in recent research is the correlation between smaller construction firms and reduced innovation. Smaller projects often lack the investment potential for impactful advancements like those seen in other industries, leading to a vicious cycle. As fewer homes are built, the ability for the construction sector to innovate and improve its efficiency declines as well. This stagnation directly contributes to the housing affordability crisis, highlighting the need for policy changes that promote larger, more efficient developments that can meet contemporary housing demands effectively.
Trends in the Housing Market
Analyzing current housing market trends reveals a stark reality: inventory levels remain low while demand continues to rise, leading to upward pressure on prices. As more individuals and families seek to purchase homes in a competitive market, the gap between supply and demand widens, ultimately exacerbating the affordability crisis. Furthermore, changing demographics and preferences among younger generations have shifted homebuyer expectations, but a lack of available listings continues to pose a significant barrier.
Market trends also show a shift in the types of properties being built, with high-density apartments and townhomes rising in popularity as families seek more affordable options. However, even these options often remain out of reach due to restrictive zoning laws and local regulations that limit development. To ensure the housing market can better reflect the needs of today’s population, a reevaluation of land-use and planning strategies is critical. Such changes are necessary to create a balanced market where all income brackets can access safe, affordable housing.
Addressing Homeownership Challenges
Homeownership has long been regarded as part of the American dream, but recent hurdles have made this milestone increasingly elusive for many. Challenges such as elevated home prices, rising interest rates, and the burdens of student debt have combined to create a formidable barrier to entry for would-be homeowners. Such financial pressures have shifted societal priorities, placing increased emphasis on renting rather than owning, which can contribute to larger economic disparities.
Targeting these homeownership challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, which includes implementing reforms to promote sustainable development and enhance access to affordable financing options. Additionally, fostering partnerships between public and private sectors can enable innovative solutions to emerge, supporting greater access to homeownership for low-income families. Addressing these issues holistically can pave the way towards achieving the goal of equitable homeownership across diverse socioeconomic groups.
The Importance of Innovative Housing Solutions
Innovation plays a crucial role in resolving the barriers to housing affordability, particularly through new construction methods and materials that enhance productivity. As the construction industry grapples with chronic stagnation, investment in technological advancements could yield significant improvements in efficiency. For instance, prefabrication and modular construction have the potential to streamline building processes, ultimately reducing costs and timeframes associated with traditional methods. As these innovations come to the forefront, they hold promise for revitalizing the housing market.
Moreover, fostering innovation in housing solutions must also include engaging with diverse stakeholders to catalyze fresh ideas, such as sustainable building practices and the adaptation of urban designs that promote density without compromising livability. Policymakers and industry leaders should champion initiatives that support research and development in housing technologies to promote resilience and affordability. By embracing an innovative mindset, the housing sector can better respond to the evolving needs of communities and help alleviate the pressing affordability crisis.
Historical Context of Housing Development
The historical context of housing development in the U.S. reveals the impact that policy decisions and market trends have had on current affordability issues. From the post-war boom of the 1950s and 60s, which led to rapid suburban development and the construction of large-scale housing projects, to the more recent emergence of regulation-heavy environments, the evolution of housing policy has shaped today’s landscape. Understanding this history is essential to identify trends and develop effective strategies for moving forward in addressing today’s challenges.
Reviewing the past also highlights pivotal moments, such as the deregulation of certain zoning laws to promote the construction of diverse housing stock during times of economic growth. However, this progress has often been stymied by local opposition to new developments, revealing a pattern where policy can swing in favor of more restrictive practices over time. Learning from historical successes and failures provides invaluable insights to support future initiatives that balance community needs with the necessity for increased housing supply.
Community Engagement and Housing Solutions
The engagement of community members in the housing development process is a critical factor in addressing the affordability crisis effectively. Raising awareness and promoting understanding of the benefits associated with new developments can help mitigate some of the fears associated with NIMBYism. Community engagement initiatives that highlight the importance of inclusive housing can foster a cooperative spirit that paves the way for successful project implementation.
Moreover, encouraging diverse voices to participate in discussions about housing solutions can ensure that community needs are heard, leading to more equitable development outcomes. As local governments face pressure to appease current residents, it is essential to incorporate the perspectives of underserved populations that may stand to benefit from new housing projects. Building bridges between developers and community members is vital for creating sustainable housing initiatives that meet the demands and expectations of modern society.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do land-use regulations contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations contribute significantly to the housing affordability crisis by limiting the size and scale of construction projects. Tighter regulations often lead to smaller developments which decrease construction productivity, increasing costs for homebuyers. This results in fewer affordable housing options and exacerbates the challenges of homeownership for many Americans.
What is NIMBYism and how does it affect the housing market trends?
NIMBYism, or ‘Not In My Backyard’ attitudes, often leads to community resistance against new housing developments, which directly impacts housing market trends. Such resistance can cause delays and increased costs for construction, ultimately contributing to the housing affordability crisis by stifling the development of needed housing supply.
What are the main challenges to homeownership in the current housing affordability crisis?
The current housing affordability crisis presents several challenges to homeownership, including soaring home prices primarily due to increased construction costs and restrictive land-use regulations. Many potential homeowners face barriers such as high down payment requirements and limited availability of affordable homes, making it increasingly difficult for them to enter the housing market.
How has construction productivity influenced the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity has declined over the decades, significantly impacting the housing affordability crisis. As land-use regulations and small-scale projects became prevalent, builders have been less incentivized to innovate, resulting in increased conventional housing costs and fewer homes being built, making it challenging for individuals to find affordable living options.
What are housing market trends that indicate an escalation in the affordability crisis?
Current housing market trends indicating an escalation in the affordability crisis include rising home prices, a decreasing number of affordable units, and slowing construction growth. These trends highlight the struggle many Americans face in achieving homeownership, often due to restrictive policies and increased building costs.
What role does construction innovation play in addressing housing affordability issues?
Construction innovation plays a crucial role in addressing housing affordability issues by improving efficiency and reducing costs. However, the decline in construction patents and innovation post-1970 suggests a stagnation in the sector. Boosting innovation could help reverse trends, making building more efficient and affordable.
How does the decline in large housing projects relate to the housing affordability crisis?
The decline in large housing projects is closely related to the housing affordability crisis. As large-scale developments have diminished, due to increased land-use regulations and NIMBYism, the construction sector has become less productive, resulting in higher housing costs and fewer affordable options for potential homeowners.
What strategies can be implemented to mitigate the housing affordability crisis?
Strategies to mitigate the housing affordability crisis may include reforming land-use regulations to encourage larger developments, promoting denser housing projects, and incentivizing innovation in construction. By addressing these areas, communities can facilitate the creation of more affordable homes and improve accessibility for aspiring homeowners.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The cost of new single-family homes has more than doubled since 1960, making home ownership increasingly unattainable for many Americans. |
| NIMBY Land-Use Policies | ‘Not in my backyard’ attitudes towards land-use regulations limit the scale of construction projects, leading to higher costs and less innovation in the housing market. |
| Decline in Construction Productivity | Between 1970 and 2000, housing construction productivity fell by 40%, despite overall economic growth during the same period. |
| Impact of Small Firms | Today’s construction firms are much smaller and less productive compared to larger firms from the mid-20th century, limiting their ability to innovate. |
| Comparison with Automotive Industry | While the auto industry saw continuous productivity growth, construction productivity has stagnated, highlighting a significant disparity. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are losing wealth through housing, as evidenced by the stark drop in average home equity for the 45-54 age group from 1983 to 2013. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue affecting millions of Americans today. With skyrocketing costs and restrictive land-use policies stifling construction productivity and innovation, homeownership is becoming increasingly elusive for many families. The intersection of NIMBY attitudes and the decline of large-scale building projects contributes significantly to this crisis, limiting options for growth and affordability in the housing sector. As the country seeks solutions, addressing these regulatory barriers will be crucial for revitalizing the housing market and restoring access to affordable homeownership for future generations.