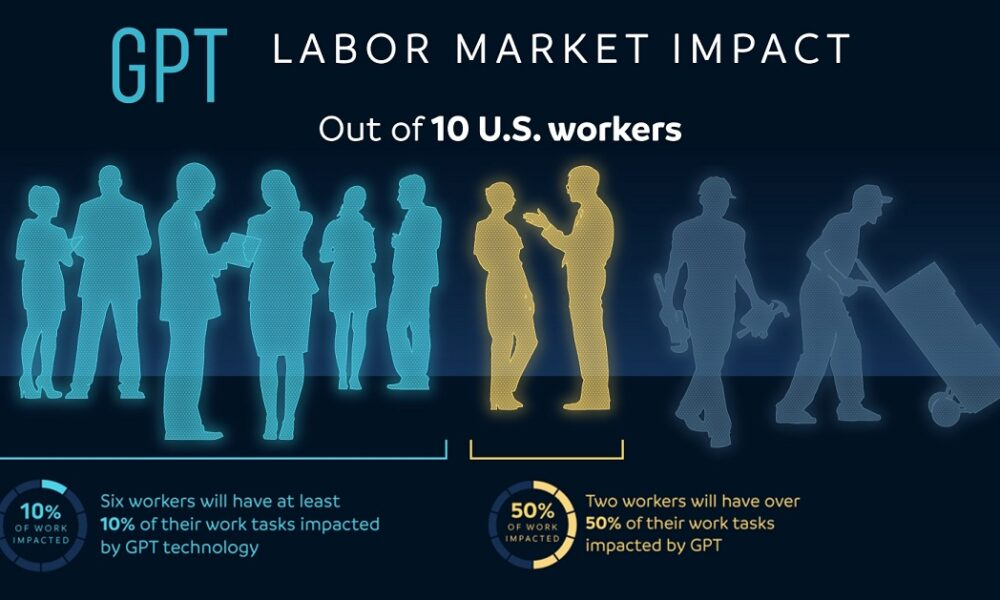
In recent years, the intersection of AI and the labor market has become a hot topic, as advancements in artificial intelligence impact workforce dynamics in profound ways. As researchers delve into job market trends, they are uncovering how automation in the workforce is reshaping traditional employment structures and creating new opportunities. Contrary to the narrative that technology is stealing jobs, some studies suggest that AI may instead be fostering growth in high-skilled roles, signaling a shift towards the future of work. The advent of technologies such as machine learning is driving significant changes, prompting debates about technology disruption jobs and the evolving landscape of employment. Understanding these trends is crucial for navigating the complexities of today’s labor market, as the implications of AI are poised to redefine how we work.
Artificial intelligence is increasingly influencing professional landscapes, stirring discussions about how it integrates with current job roles and employment trends. The integration of advanced technologies into various sectors hints at a transformation in the nature of work, leading to fluctuations within the job market. While some worry about potential job losses, a more nuanced view reveals that this technological evolution could instead lead to the creation of new, specialized positions. As the concept of automation infiltrates across industries, it becomes essential to explore how these innovations are modifying work practices and opportunities. Preparing for the future of labor requires an understanding of both the benefits and challenges posed by AI in shaping the workforce.
Understanding the Evolution of the Labor Market with AI
Over the last century, the emergence of new technologies has continually reshaped the U.S. labor market. From the advent of the telephone to the rise of computers, each innovation has brought about significant changes in employment patterns. Recent research indicates that artificial intelligence (AI) is the latest in a line of breakthrough technologies that profoundly impact job distribution and skills requirements. While previous generations experienced substantial occupational churn driven by automation and technological advancement, the current era of AI is poised to redefine job roles, particularly in knowledge-based sectors.
The study conducted by Harvard economists reveals that AI’s integration into various industries signals a shift away from traditional job structures, emphasizing the need for workers to adapt to new skill demands. With occupations increasingly driven by technological capabilities, individuals with high levels of training in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) are seeing growth in their employment opportunities. This represents a shift from a barbell labor market towards one that prioritizes tech-savvy individuals, highlighting the essential role of AI in transforming workforce dynamics.
The Four Trends Emerging from AI Integration
The authors of the study identify four key trends resulting from AI’s incorporation into the labor market. The first is the decline of job polarization, where a noticeable preference emerges for high-paid, skilled positions over low-paid roles. As organizations integrate AI tools into their operations, the demand for talent capable of leveraging these technologies intensifies. Consequently, while jobs at the bottom of the wage scale are still prevalent, the focus on high-skill roles signifies a recalibration of the job market that could leave unskilled workers at a disadvantage.
Additionally, the rise of STEM professions points to the increasing importance of technical skills in a digital-first economy. With the share of STEM jobs rising significantly since 2010, organizations are not only hiring more specialized talent but also investing heavily in AI-driven technologies. This trend underscores how AI is not simply replacing jobs but reshaping them, requiring a workforce that can adapt and thrive in an increasingly automated environment. As Deming noted, the data reveals a clear trajectory that suggests major workforce transitions are underway.
The Impact of Automation on Job Distribution
AI’s role in automation is reshaping various sectors, particularly within the low-paid service and retail industries. The study highlights that since 2019, there has been a notable decline in low-paid service jobs, marking a significant shift from previous years when such positions were on the rise. This could be attributed to the growing capabilities of AI tools and their integration into customer service functions, effectively reducing human roles. As AI technologies evolve, the need for human interactivity in certain service-based sectors may diminish, exemplifying the challenges faced by lower-skilled workers in adapting to these rapid changes.
Moreover, the retail sector has experienced a significant contraction in jobs, with e-commerce and AI technologies altering traditional shopping behaviors. As more consumers turn to online shopping facilitated by AI insights and predictive analytics, retail positions are diminishing, driving a transformation in job roles and expectations. This not only reflects changing consumer habits accelerated by the pandemic but also raises concerns about job sustainability in an era where technological disruption appears inevitable. Companies may prioritize investment in AI systems over human labor, reinforcing the necessity for workers to embrace lifelong learning and skill advancement.
Adapting to a High-Tech Workforce
The integration of AI in the labor market underscores the importance of adaptability among workers, particularly in tech-heavy fields. As employers increasingly seek individuals who possess the ability to work alongside advanced technologies, the significance of continuous learning becomes apparent. Knowledge workers in sectors like finance and management must be proactive in developing skills that complement AI processes to remain competitive. The shift towards performance efficiency driven by AI means that traditional expectations of job delivery will evolve, compelling workers to produce results at an unprecedented pace.
Employers may begin to favor candidates who exhibit not only technical capabilities but also an aptitude for change and innovation in their roles. This highlights the necessity for educational initiatives that empower individuals with the requisite skills to thrive in an AI-driven economy. As organizations grapple with the implications of AI on productivity and job fulfillment, a culture of continuous professional development will be crucial in preparing the workforce for future changes in job landscape. Thus, embracing a mindset geared towards adaptability becomes integral to navigated the complexities of the future of work.
The Dual Edge of AI Empowerment and Job Displacement
As AI tools become more integrated into various sectors, they present both opportunities and challenges for modern workers. On one side, AI has the potential to empower employees by enhancing productivity and facilitating new ways of working. As noted by Summers, the impact of AI may lead to more efficient practices, enabling workers to achieve more in less time. This empowerment can boost overall job satisfaction and drive organizational success when properly harnessed.
Conversely, the looming threat of job displacement due to automation creates anxiety within the labor market. Occupations that once seemed stable may become vulnerable as companies adopt AI solutions that outperform traditional roles. Knowledge workers must recognize this dual-edge nature of AI; while it can enhance their capabilities, it also necessitates a commitment to ongoing education and skill development to mitigate the risk of being replaced. The challenge lies in balancing the benefits of AI with the need for human skills in domains that require creativity, empathy, and critical thinking.
Job Market Predictions in the Age of AI
Predicting the labor market in an age increasingly influenced by AI requires a comprehensive analysis of trends currently shaping employment. The research highlights a notable shift in job distribution, with high-demand positions emerging primarily in technical fields. This development suggests that the future job market will be less about quantity and more about the quality and relevance of skills possessed by the workforce. Organizations will likely seek professionals who can leverage AI systems in decision-making processes and strategic implementation.
Experts argue that the job market is entering a phase where adaptability and responsiveness to technological innovation will be critical. Workers who identify and embrace emerging technologies stand to benefit from new career paths created by AI integration. However, the emphasis on technical skills must not overshadow the need for soft skills, as human judgment, creativity, and interpersonal capabilities will remain invaluable in a machine-driven economy. The trajectory towards a new era of work demands that employees maintain a holistic approach to skill development.
Challenges Faced by Low-Paid Workers in a Tech-Driven Economy
For low-paid workers, the rise of AI and automation presents unique challenges that could exacerbate existing inequalities in the labor market. As companies increasingly rely on AI to streamline operations and reduce costs, many positions traditionally filled by human employees may become obsolete. The decline in low-paid service jobs, as noted in the Harvard study, indicates that without concerted efforts to upscale and reskill these workers, a significant portion may find themselves displaced from the job market altogether.
While some workers may transition to roles in industries poised for growth, there remains a considerable risk that those without access to training and education will struggle to adapt. Community initiatives and government support programs will play an essential role in helping low-paid workers acquire the necessary skills to thrive in an evolving job landscape, as AI continues to redefine the future of work. Failure to address these disparities could result in a more polarized workforce, with significant implications for economic stability and social cohesion.
The Future of Work: Balancing Technology and Human Talent
As we advance further into an AI-infused economy, a critical question arises: how can organizations strike a balance between leveraging technology and preserving human talent? The unprecedented pace of technological advancements necessitates a reevaluation of priorities within the workforce. Businesses that effectively integrate AI while simultaneously recognizing the irreplaceable value of human intelligence will likely find the greatest success in the future job market. Innovating without alienating staff is essential for fostering sustainable growth.
Moreover, the ability to cultivate a culture that embraces both AI and human insights will be integral in navigating upcoming workforce transformations. As mentioned earlier, the demand for creativity and human interaction will persist even in an automated landscape. Companies that can successfully amalgamate the efficiency of AI with the emotional intelligence of their teams will not only thrive but also create a more resilient and adaptable workforce, ready to face the challenges and opportunities the future of work will undoubtedly present.
Preparing for a Future Driven by AI Innovations
In preparing for a future shaped by artificial intelligence innovations, organizations and individuals alike must adopt a proactive approach to education and skill enhancement. Employers will be crucial in facilitating ongoing learning opportunities that focus on AI literacy for their employees. By ensuring that workers have access to training programs and resources aimed at developing their digital competencies, firms can cultivate a more agile and adaptable workforce primed for the challenges that technology disruptions will bring.
Simultaneously, individuals must also take ownership of their career trajectories by pursuing continuous education and skill-building initiatives. As the labor market evolves, being adaptable and ready to acquire new skills will be essential for career longevity. By recognizing the value of blending technical expertise with traditional skills, workers can position themselves for success in an increasingly automated world, where the relationship between humans and technology will be more intertwined than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is artificial intelligence impacting the labor market today?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is significantly reshaping the labor market by driving changes in occupational churn and creating new job trends. Economists have found that recent investments in AI are changing job distributions, particularly favoring high-skilled, high-paying positions, while traditional low-paid service jobs are experiencing decline.
What job market trends are emerging due to AI and technology disruption?
Emerging job market trends linked to AI include a rise in STEM job opportunities, an end to job polarization with growth primarily in high-wage sectors, and a notable decline in low-skilled service and retail jobs. This reflects a shift where technologically skilled workers are in higher demand as firms invest in new AI technologies.
What is the relationship between automation and workforce changes?
Automation is significantly altering the workforce by increasing productivity and changing the skill set required for many jobs. While it can lead to job displacement, particularly in low-skill areas, it is also creating new opportunities for those skilled in technology and AI.
How has AI contributed to job volatility in the economy?
AI has contributed to job volatility by accelerating the rate at which certain occupations are becoming obsolete, particularly in sectors like retail and low-wage services. As firms increasingly rely on AI for efficiency, the demand for traditional jobs declines, leading to higher volatility in the job market.
What does the future of work look like with AI integration?
The future of work is likely to involve greater emphasis on technology skills, with AI enabling faster productivity. Knowledge work may transform significantly as companies expect more immediate outputs from employees adept at using AI tools, highlighting the need for continuous upskilling.
Is AI likely to replace jobs in the near future, and what should workers do?
While AI is poised to replace certain job categories, particularly those involving repetitive tasks, workers should focus on developing skills that leverage AI technologies. Upskilling in critical thinking, creativity, and advanced tech will be essential to thrive in an AI-driven labor market.
What sectors are most affected by AI’s influence on jobs?
Sectors such as retail, low-paid services, and certain manufacturing roles are most affected as AI and automation increase operational efficiency and reduce labor costs. Meanwhile, industries requiring advanced technical skills, such as IT and engineering, are seeing growth.
How can businesses adapt to AI’s transformation of the labor market?
Businesses can adapt to AI’s transformation by investing in employee training, fostering a culture of continuous learning, and integrating AI technologies into workflows. This approach helps them remain competitive and prepares their workforce for the future demands of the labor market.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview of Study | Conducted by David Deming and Lawrence Summers; analyzed 100+ years of U.S. labor market changes due to technology. |
| Historical Context | A period of stability (1990-2017) conceals the impact of earlier technological disruptions. |
| Recent Trends Identified | AI is driving significant changes in occupational structures and job distribution. |
| Job Polarization | Shift from a barbell pattern in job quality to growth in high-paid jobs requiring advanced skills. |
| STEM Job Growth | Increase from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, highlighting demand for technical skills. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Jobs | Employment in low-paying service roles is stagnant or declining post-2019. |
| Impact on Retail Jobs | Retail sales jobs fell by 25% from 2013 to 2023, accelerated by e-commerce and AI. |
| Future Implications | AI may boost productivity but poses displacement risks for knowledge workers. |
Summary
AI and the labor market are undergoing significant transformations as illustrated by recent research conducted by Harvard economists. The study reveals that artificial intelligence is reshaping the workforce in unprecedented ways, marking a shift from previous periods of stability. It highlights emerging trends such as job polarization, growth in STEM-related positions, and a decline in low-wage jobs, indicating that while AI enhances productivity, it also introduces potential challenges in job security and displacement for many workers. As we move forward, adapting to these changes will be essential for navigating the evolving landscape of employment in the age of AI.